Treatments for Secondary Liver Cancer
Secondary liver cancer is caused by the primary cancer of some other part of the body. The cancer cells that spread to the liver from the primary cancer of other parts, such as the pancreas, breasts, stomach, or lungs cause secondary liver cancer. The treatment for secondary liver cancer will be decided based on where the cancer came from and the level of cancer spread. Herein, we discuss the common treatment options for secondary liver cancer:
1. Surgery
Surgery is not performed on everyone because it depends on how far the cancer has spread. It makes sure whether you only have secondary cancer in the liver or if the cancer has spread to any other part of the body. If the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, surgery is not suggested in the case of secondary liver cancer.
2. Hepatic artery infusion (HAI)
The process of giving chemotherapy directly into the hepatic artery going into the liver is known as hepatic artery infusion (HAI). The catheter is inserted into the main artery leading to the liver. In HAI, a high concentration of the chemotherapy drug is injected to get to the tumor. Every people with secondary liver cancer is not suitable for this treatment. However, HAI will be performed by the doctor only if your conditions fulfill certain criteria.
3. Hormone therapy
Some cancers including secondary liver cancer depend on hormones to grow and survive. Hormone therapy helps in lowering hormone levels in the body and destroys the cancer cells. Hormone therapy may be performed with tablets or injections.
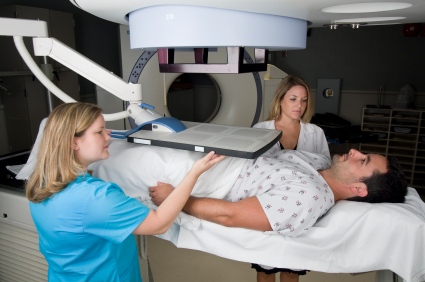
4. Radiotherapy
This treatment is a process of using high energy waves to destroy cancer cells. The liver is sensitive to radio waves, so radiotherapy is not initially performed for the treatment of liver cancer. However, in the case of secondary liver cancer, radiotherapy helps in controlling further growth and spread of cancer cells. It also helps in controlling the pain. There are various types of radiotherapy. They are
- Selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT)
SIRT is a type of internal radiotherapy, otherwise known as brachytherapy. In SIRT, the catheter is inserted into the artery of the liver (hepatic artery) which supplies blood to the liver. Tiny beads called microspheres are sent down the catheter, and these microspheres will get hold of the small blood vessels around the tumor. This process gives radiation to the tumor through the microspheres that contain a radioactive substance. This radiation restricts the blood supply to the tumor and helps in destroying the cancerous cells. This process of destroying the blood supply to the tumor through the microspheres is sometimes called radioembolization. - External beam radiation therapy (EBRT)
EBRT is the most commonly used type of radiation therapy. In EBRT, the radiation is delivered via a machine from outside the body to the tumor or cancer cells. It is the most painless treatment for cancer and is very effective in treating other types of cancers, including that of the secondary liver. Only in recent years, EBRT is being used to treat liver cancer. It is because EBRT is difficult to perform in the case of liver cancer because the liver moves with every breath. However, with the latest improvements in technology, EBRT is considered safe and easy to treat liver cancer as well. - Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT)
SBRT is also similar to other radiation therapy. It is a new technology that delivers a high dose of radiation using an EBRT machine.




